The UK Emissions Trading Scheme was a voluntary emissions trading system created as a pilot prior to the mandatory European Union Emissions Trading Scheme. It ran from 2002 and closed in 2006.
At the time, the scheme was a novel economic approach, being the first multi-industry carbon trading system in the world. (Denmark ran a pilot greenhouse gas trading scheme between 2001 and 2003 but this only involved eight electricity companies). It took note of the emerging international consensus on the benefits of carbon trading that were being proposed in the mandatory Kyoto Protocol, which had not been ratified at that time, and allowed government and corporate early movers and to gain experience in the auction process and the trading system that the later schemes have entailed. It ran in parallel to a tax on energy use, the Climate Change Levy, introduced in April 2001, but companies could get a discount on the tax if they elected to make reductions through participation in the trading scheme.
The voluntary trading scheme recruited 34 participants from UK industries and organisations who promised to make reductions in their carbon emissions. In return they received a share of a £215 million "incentive fund" from the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA). Each agreed to hold sufficient allowances to cover its actual emissions for that year, and participate in a cap and trade system, with an annually-reducing cap. Each participant could then decide to take action to manage its emissions to exactly meet its target, or reduce its actual emissions below its target (thereby releasing allowances that it could sell on, or save for use in future years), or buy allowances from other participants to cover any excess.
From March 2002, DEFRA ran an auction of emission allowances to perform allocations to participants, until the scheme closed in 2006, after the start of the mandatory EU scheme.
Conclusions
The UK's National Audit Office and DEFRA's consultants ran reviews of the system in order to establish its basis and drew lessons from it.
They concluded that the scheme did achieve some emission reductions from the participants, although more could have been achieved had targets been more demanding.
* The 34 companies that participated took advantage of the incentive fund to pay for reduction measures, and in practice most were incentivised to make additional efforts to further cut emissions beyond their targets. They gained experience in pricing strategies and were prepared in advance of the start of the mandatory scheme.
* The companies that provided emissions trading brokerage and verification were able to establish their new businesses in the UK, and have since translated that first mover advantage to establish themselves on the European and wider international trading arena.
* DEFRA discovered the issues and practicalities of negotiating and setting baselines and running an auction process.
* the lessons learned also influenced the EU's confidence to proceed in the EU ETS.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Tampilkan postingan dengan label Carbon emissions trading schemes. Tampilkan semua postingan
Tampilkan postingan dengan label Carbon emissions trading schemes. Tampilkan semua postingan
Sabtu, 05 Desember 2009
Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative
Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI, or ReGGIe) is a regional initiative by states and provinces in the Northeastern United States region to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The RGGI is designing a cap and trade program for greenhouse gas emissions from power plants.
Ten states currently participate in the initiative. Pennsylvania, which is a major coal producer and manufacturing state, only participates as an observer.
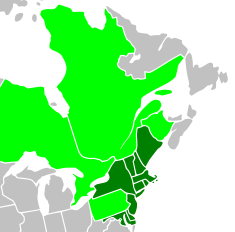
Current membership
* Participating states: Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Massachusetts, Maryland, Rhode Island
* Observer states and regions: Pennsylvania, District of Columbia, Québec, New Brunswick, Ontario.
Implementation
RGGI is implementing a cap and trade system for CO2 emissions from power plants in the member states. Emission permit auctioning began in September 2008, and the first three-year compliance period began on January 1, 2009. Proceeds will be used to promote energy conservation and renewable energy. The system affects fossil fuel power plants with 25 MW or greater generating capacity ("compliance entities").
Climate Change Action Plan
A parallel effort to reduce emissions in the Northeast is the New England Governors/Eastern Canadian Premiers Climate Change Action Plan, which calls for a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions to 10% below 1990 levels by 2020. For comparison: the EU aims to reduce emissions to 20% below 1990 levels by 2020.
In addition, the Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management (NESCAUM) is building a Regional Greenhouse Gas Registry (RGGR) to help track emissions in the region. This effort is similar to that of the California Climate Action Registry.
Carbon auction
The Memorandum of Understanding commits states to invest 25% of revenue from carbon credits to energy efficiency and strategic energy schemes. This revenue is received by auctioning credits from the state budget to compliance entities. Since signing the MOU in 2005, all ten states have committed in their Model Rule to the sale of the vast majority of the state's carbon budget. This overcomes the problem of opportunity cost associated with the EU ETS, which led to windfall profits for generators.
RGGI sold carbon credits on Thursday September 25, 2008 in the first of a series of quarterly online auctions. 12,565,387 allowances were sold for $3.07 per ton of carbon dioxide, bringing in a total of $38,575,738.09. It was the largest carbon auction at the time. The second auction was held December 17, 2008. 31,505,898 allowances were sold for $3.38 per allowance. In the third auction, held on March 18, 2009, 31,513,765 (2009) allowances were sold for $3.51 per allowance, and 2,175,513 (2012) allowances were sold for $3.05 per allowance. The June 17 saw 30.8 million allowances sold for $3.23 per allowance, and 2.17 million 2012 allowances sold for $2.06.
History
In 2003 George Pataki, then Governor of New York, sent a letter to the governors of Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states seeking "to develop a strategy that will help the region lead the nation in the effort to fight global climate change."
In August 2005, the RGGI staff working group proposed an emissions reduction program that would start in 2009 and lead to a stabilization of emissions at current levels (an average of 2002-2004 levels) by 2015. This would be followed by a 10% reduction in emissions between 2015 and 2020. The proposal would also allow participants to purchase offsets to meet 50% of their emission reductions.
As of December 20, 2005, seven Northeastern US states were involved in the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative. Massachusetts and Rhode Island dropped out at the last minute; Massachusetts Governor Mitt Romney objected to a lack of opt-out provisions if energy prices exceeded a certain threshold.. He went on to attack Senator John McCain for his positive position on cap-and-trade during the 2008 presidential election. The seven states still involved (Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, Vermont, New Hampshire and Maine) signed a "Memorandum of Understanding" committing themselves to move forward with the program. Special provisions were made in that document for Massachusetts and Rhode Island to join the effort at any time prior to January 1, 2008.
Massachusetts rejoined on January 18, 2007, on the order of newly elected Governor Deval Patrick.
Rhode Island rejoined on January 30, 2007. Governor Donald L. Carcieri used his State of the State address to make the announcement. While he reiterated his concern about the impact on energy costs, he said that "I have been assured that those costs can be offset by credits we will receive from other states."
On April 20, 2007, Maryland Governor Martin O’Malley signed an agreement to join, making Maryland the 10th state to join the initiative.
New Hampshire joined on June 12, 2008, when Gov. John Lynch signed a law implementing RGGI.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Ten states currently participate in the initiative. Pennsylvania, which is a major coal producer and manufacturing state, only participates as an observer.

Current membership
* Participating states: Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Massachusetts, Maryland, Rhode Island
* Observer states and regions: Pennsylvania, District of Columbia, Québec, New Brunswick, Ontario.
Implementation
RGGI is implementing a cap and trade system for CO2 emissions from power plants in the member states. Emission permit auctioning began in September 2008, and the first three-year compliance period began on January 1, 2009. Proceeds will be used to promote energy conservation and renewable energy. The system affects fossil fuel power plants with 25 MW or greater generating capacity ("compliance entities").
Climate Change Action Plan
A parallel effort to reduce emissions in the Northeast is the New England Governors/Eastern Canadian Premiers Climate Change Action Plan, which calls for a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions to 10% below 1990 levels by 2020. For comparison: the EU aims to reduce emissions to 20% below 1990 levels by 2020.
In addition, the Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management (NESCAUM) is building a Regional Greenhouse Gas Registry (RGGR) to help track emissions in the region. This effort is similar to that of the California Climate Action Registry.
Carbon auction
The Memorandum of Understanding commits states to invest 25% of revenue from carbon credits to energy efficiency and strategic energy schemes. This revenue is received by auctioning credits from the state budget to compliance entities. Since signing the MOU in 2005, all ten states have committed in their Model Rule to the sale of the vast majority of the state's carbon budget. This overcomes the problem of opportunity cost associated with the EU ETS, which led to windfall profits for generators.
RGGI sold carbon credits on Thursday September 25, 2008 in the first of a series of quarterly online auctions. 12,565,387 allowances were sold for $3.07 per ton of carbon dioxide, bringing in a total of $38,575,738.09. It was the largest carbon auction at the time. The second auction was held December 17, 2008. 31,505,898 allowances were sold for $3.38 per allowance. In the third auction, held on March 18, 2009, 31,513,765 (2009) allowances were sold for $3.51 per allowance, and 2,175,513 (2012) allowances were sold for $3.05 per allowance. The June 17 saw 30.8 million allowances sold for $3.23 per allowance, and 2.17 million 2012 allowances sold for $2.06.
History
In 2003 George Pataki, then Governor of New York, sent a letter to the governors of Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states seeking "to develop a strategy that will help the region lead the nation in the effort to fight global climate change."
In August 2005, the RGGI staff working group proposed an emissions reduction program that would start in 2009 and lead to a stabilization of emissions at current levels (an average of 2002-2004 levels) by 2015. This would be followed by a 10% reduction in emissions between 2015 and 2020. The proposal would also allow participants to purchase offsets to meet 50% of their emission reductions.
As of December 20, 2005, seven Northeastern US states were involved in the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative. Massachusetts and Rhode Island dropped out at the last minute; Massachusetts Governor Mitt Romney objected to a lack of opt-out provisions if energy prices exceeded a certain threshold.. He went on to attack Senator John McCain for his positive position on cap-and-trade during the 2008 presidential election. The seven states still involved (Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, Vermont, New Hampshire and Maine) signed a "Memorandum of Understanding" committing themselves to move forward with the program. Special provisions were made in that document for Massachusetts and Rhode Island to join the effort at any time prior to January 1, 2008.
Massachusetts rejoined on January 18, 2007, on the order of newly elected Governor Deval Patrick.
Rhode Island rejoined on January 30, 2007. Governor Donald L. Carcieri used his State of the State address to make the announcement. While he reiterated his concern about the impact on energy costs, he said that "I have been assured that those costs can be offset by credits we will receive from other states."
On April 20, 2007, Maryland Governor Martin O’Malley signed an agreement to join, making Maryland the 10th state to join the initiative.
New Hampshire joined on June 12, 2008, when Gov. John Lynch signed a law implementing RGGI.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Jumat, 04 Desember 2009
New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme
The New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (NZ ETS) is a largely proposed all-sectors all-gases emissions trading scheme established in September 2008 by the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand. Most of the provisions of the NZ ETS have not yet taken effect as the NZ ETS includes delayed entry dates. The election of the National Government in November 2008 has further delayed the effect of the NZ ETS.
Only the forestry sector has entered the NZ ETS. Carbon credits have been earned by forestry for carbon sequestration and have been sold internationally. In September 2009, South Island forestry company Ernslaw One sold about 500,000 carbon credits (valued at more than $NZ10 million) to the Norwegian Government.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Only the forestry sector has entered the NZ ETS. Carbon credits have been earned by forestry for carbon sequestration and have been sold internationally. In September 2009, South Island forestry company Ernslaw One sold about 500,000 carbon credits (valued at more than $NZ10 million) to the Norwegian Government.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Kamis, 03 Desember 2009
Climate Stewardship Acts
The Climate Stewardship Acts are a series of three acts introduced to the United States Senate by Senator John McCain (R-AZ) and Senator Joseph Lieberman (ID-CT), with a number of other co-sponsors. Their aim was to introduce a mandatory cap and trade system for greenhouse gases, as a response to the threat of anthropogenic climate change. All three acts failed to gain enough votes to pass through the senate.
2003 Climate Stewardship Act
The first Act (S. 139, H.R. 4067) was defeated in the U.S. Senate by 55 votes to 43.
If passed, it would have capped 2010 CO2 emissions at the 2000 level. Residential and agricultural areas, as well as other areas deemed "not feasible", would be exempt. As such, approximately 85% of the United State's emissions would have been covered for the year 2000. The bill would have also established a scholarship at the National Academy of Sciences for those studying climatology.
2005 Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act
Under a slightly modified title, but with similar provisions, the Act (S. 1151) was reintroduced to a new Congress. The Act now called for the federal government to play a lead role in researching and commercialising new energy technologies, and particularly nuclear plant designs. The bill was defeated 38 Yea to 60 Nay.
2007 Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act
The substantional strengthening of this Act (S. 280) involved the provision for the emissions cap, immobile in previous Acts, to be gradually reduced, following the theory of contraction and convergence. It was co-sponsored by eleven senators and also received endorsements from the National Wildlife Federation, Environmental Defense, and the Pew Center on Global Climate Change.
Reductions in emissions under the Act would be to 2004 levels by 2012, 1990 levels by 2020, and 60% below 1990 by 2050. The 60% target is the level posited for the forthcoming UK Climate Change Bill.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
2003 Climate Stewardship Act
The first Act (S. 139, H.R. 4067) was defeated in the U.S. Senate by 55 votes to 43.
If passed, it would have capped 2010 CO2 emissions at the 2000 level. Residential and agricultural areas, as well as other areas deemed "not feasible", would be exempt. As such, approximately 85% of the United State's emissions would have been covered for the year 2000. The bill would have also established a scholarship at the National Academy of Sciences for those studying climatology.
2005 Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act
Under a slightly modified title, but with similar provisions, the Act (S. 1151) was reintroduced to a new Congress. The Act now called for the federal government to play a lead role in researching and commercialising new energy technologies, and particularly nuclear plant designs. The bill was defeated 38 Yea to 60 Nay.
2007 Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act
The substantional strengthening of this Act (S. 280) involved the provision for the emissions cap, immobile in previous Acts, to be gradually reduced, following the theory of contraction and convergence. It was co-sponsored by eleven senators and also received endorsements from the National Wildlife Federation, Environmental Defense, and the Pew Center on Global Climate Change.
Reductions in emissions under the Act would be to 2004 levels by 2012, 1990 levels by 2020, and 60% below 1990 by 2050. The 60% target is the level posited for the forthcoming UK Climate Change Bill.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Selasa, 01 Desember 2009
Climate change credit
The Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act
The Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act of 2005 (S.1151) was introduced jointly by US Senators John McCain (R-AZ) and Joseph I. Lieberman (D-CT). Beginning in 2010, The Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act would limit (to the amount emitted in the year 2000) the total greenhouse gases emitted by:
* U.S. electricity generation,
* Cars, busses, trains, and other forms of transportation,
* Industry
* Commerce
According to pewclimate.org, these affected sectors represented approximately 85% of the overall U.S. emissions in the year 2000. This bill also would provide for the trading of emission allowances and reductions as Climate Change Credits.
Climate Change Credit Corporation
Allocation of special Emission Permits by the Climate Change Corporation created by the Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act will provide funding for assistance for consumers and industry to fully comply with the act. Permits will be allocated to support the activities of a Climate Change Credit Corporation, a combination public and private agency that will oversee the cap and trade program, provide credit (Climate Change Credits) to participating entities for reductions in the total greenhouse gases made before 2012, and to facilitate transition for industries with competitiveness concerns and fewer options for efficient energy reduction technology. These credits are limited but can be used, bought, or sold.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
The Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act of 2005 (S.1151) was introduced jointly by US Senators John McCain (R-AZ) and Joseph I. Lieberman (D-CT). Beginning in 2010, The Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act would limit (to the amount emitted in the year 2000) the total greenhouse gases emitted by:
* U.S. electricity generation,
* Cars, busses, trains, and other forms of transportation,
* Industry
* Commerce
According to pewclimate.org, these affected sectors represented approximately 85% of the overall U.S. emissions in the year 2000. This bill also would provide for the trading of emission allowances and reductions as Climate Change Credits.
Climate Change Credit Corporation
Allocation of special Emission Permits by the Climate Change Corporation created by the Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act will provide funding for assistance for consumers and industry to fully comply with the act. Permits will be allocated to support the activities of a Climate Change Credit Corporation, a combination public and private agency that will oversee the cap and trade program, provide credit (Climate Change Credits) to participating entities for reductions in the total greenhouse gases made before 2012, and to facilitate transition for industries with competitiveness concerns and fewer options for efficient energy reduction technology. These credits are limited but can be used, bought, or sold.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Senin, 30 November 2009
Chinese national carbon trading scheme
The Chinese national carbon trading scheme was announced in November 2008 by the national government to enforce a compulsory carbon trading scheme across the country's provinces as part of its strategy to create a "low carbon civilisation".
The scheme would allow provinces to earn money by investing in carbon capture systems in those regions that fail to invest in the technology.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
The scheme would allow provinces to earn money by investing in carbon capture systems in those regions that fail to invest in the technology.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Minggu, 29 November 2009
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme
The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme is a cap-and-trade system of emissions trading for anthropogenic greenhouse gases, due to be introduced in Australia in 2010 by the Rudd government, as part of its climate change policy, marking a change in the Energy policy of Australia. The process formally began when the then Federal Labor opposition and the six Labor controlled states commissioned an independent review on energy policy the Garnaut Climate Change Review which published a number of reports. Labor, after winning federal government, then published a Green paper for discussion and comment. The Federal Treasury then modelled some of the financial and economic impacts of the proposed scheme. The Rudd Government published a final White paper on 15 December 2008. The draft legislation is the next step. After a period for comment the legislation will be introduced and likely passed in the House of Representatives where the government has a majority. After being passed there it will be submitted to the Senate. In the Senate, the Government will need the support of a number of other senators, from the Greens, Liberals, Nationals or Independents. The Government has announced that the legislation is intended to take effect in July 2010.
History
In the election year of 2007, both the Liberal-led Coalition government and the Labor opposition promised to introduce carbon trading. Opposition leader Rudd commissioned the Garnaut Climate Change Review on 30 April, while Prime Minister John Howard announced his own plan on 4 June, after the final report of the Prime Ministerial Task Group on Emissions Trading. Labor won the election on 24 November.
Green Paper
The draft Garnaut Report, issued on 4 July, was only one of many inputs into the policy-making process. The Labor government issued a "Green Paper" on 16 July, describing the intended design of the carbon trading scheme. Draft legislation will be released in December 2008, to become law in 2009.
The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme, as outlined in the Green Paper, is a market-based approach to greenhouse gas pollution, to be implemented in 2010 (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 9). The main concern for the Australian government at present is getting the design of such a scheme correct, in order that it will complement the integrated economic policy framework, and need to be consistent with the Government’s commercial strategy (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 10).
The objective of the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme is to meet Australia’s emissions reduction targets in the most flexible and cost-effective way; to support an effective global response to climate change; and to provide for transitional assistance for the most affected households and firms (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 14).
The basis of a Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme is a cap and trade system, and is a way of limiting greenhouse gas pollution, as well as giving individuals and businesses incentives to reduce their emissions (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 11). The first step for the Australian Government is to set a cap on carbon emissions, which must be consistent with longer term goals of reducing Australia’s emissions by 60% compared with 2000 levels by 2050 (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 11).
There are two definite elements of the cap and trade scheme: the cap itself, and the ability to trade (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). The cap is the limit on greenhouse gas emissions imposed by the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme. The system aims at achieving the environmental outcome of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the idea being that capping emissions creates a price for carbon and the ability to trade assures that emissions are reduced at the lowest possible price (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). Setting a limit means that the right to emit greenhouse gases becomes scarce, and scarcity entails a price. The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme will put a price on carbon in a systematic way throughout the economy (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13).
The ‘covered’ sectors are emissions that are subject to the cap, which are specified by the Government under the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). Once this is established, and after setting the cap, the Government then issues permits that are equal to the cap. The Green Paper gives the example “if the cap were to limit emissions to 100 million tonnes of Co2-e in a particular year, 100 million ‘permits’ would be issued that year” (2008, 12). With each tonne of emissions from a firm that is responsible for emissions covered by the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme, they are required to acquire and surrender a permit (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). As yet there are no limits or caps imposed on individual emitters or sectors.
There are around 1,000 firms that are under obligations from the Scheme, which covers the bulk of national emissions. This means that 99% of all firms in Australia will not need to purchase permits for their emissions.
However, the price of emissions resulting from the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme will increase the cost of those goods and services that are most emissions intensive (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13). This means that there will be a change across the prices of goods and services across the economy, reflecting how emission-intensive the goods or service is. This therefore provides businesses and consumers with incentives to use and invest in low-emissions technologies.
The second essential element of a cap and trade scheme is the ability to trade. Since carbon pollution permits will be tradeable, the price of permits will be determined by the market (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13). The main idea behind this part of the scheme is that a firm who can undertake abatement more cheaply than the permit price will do so, and that a company will pay for permits if the cost to it of lowering its emissions exceeds the cost of the permits. By trading among themselves, firms achieve the scheme cap at the least cost to the economy (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13).
The cap will only achieve the desired environmental objectives if it is enforced. This means that firms responsible for emissions covered by the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme must monitor their emissions and report them accurately to government (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). Arrangements for the assurance of reported emissions data are required.
Treasury report on the economics of climate change mitigation
The Australian Treasury's report on the economics of climate change mitigation was released on October 30, 2008. The report is considered a key input for determining the structure and targets for the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme.
The Treasury’s modeling demonstrated that early global action to reduce carbon emissions would be less expensive than later action and stated that a market-based approach allows robust economic growth into the future as emissions fall.
The report also stated that:
* many of Australia’s industries would maintain or improve their competitiveness under an international agreement to combat climate change
* even ambitious goals would have limited impact on national and global economic growth
* Australia and the world can continue to prosper while making the emission cuts required to reduce the risks of dangerous climate change.
* Households would face increased prices for emission-intensive products such as electricity and gas, however real household income would continue to grow.
* Strong coordinated global action would reduce the economic cost of achieving environmental objectives, reduce distortions in trade-exposed sectors, and provide insurance against climate change uncertainty.
* There are advantages to Australia acting early if emission pricing expands gradually across the world: economies that defer action face higher long-term costs, as global investment is redirected to early movers.
* Australia’s aggregate economic costs of mitigation are small, although the costs to sectors and regions vary. Growth in emission-intensive sectors slows and growth in low- and negative-emission sectors accelerates.
* Allocation of some free permits to emission-intensive trade-exposed sectors, as the Government proposes, eases their transition to a low-emission economy in the initial years.
* Broadly-based market-oriented policies, such as emissions trading, allow the market to respond as new information becomes available.
White Paper
The White Paper was released on 15 December 2008. The White Paper included the Rudd Labor government's targets for Greenhouse gas emission reductions, 5% below 2000 by 2020 on a unilateral basis or up to 15% below 2000 by 2020 if also agreed by the other major emitters. This compares to the 25 to 40% cut compared to 1990 emissions recommended by the IPCC as needing to be made by developed countries to keep CO2 below 450 ppm and to have a reasonable chance of keeping global warming at less than a 2 degree Celsius increase above pre-industrial times.
The White Paper also set an indicative national emissions trajectory for the first few years of the scheme:
* in 2010-11, 109% of 2000 levels;
* in 2011-12, 108% of 2000 levels;
* in 2012-13, 107% of 2000 levels.
For comparison, in 2006, Australia's emissions were 104% of 2000 levels (under Kyoto accounting).
Some of the features of the emissions trading scheme proposed include:
1. an output as opposed to consumption based scheme
2. A modelled carbon price range of AUD 20 to AUD 40 per tonne of carbon.
3. Less than 1,000 businesses will have to account for their emissions and buy or be allocated free permits.
4. AUD 4.8 billion of assistance (in the form of free permits) for the most polluting electricity generators.
5. Financial assistance to compensate low and middle income families from increased costs.
6. Free permits to emissions-intensive, trade-exposed businesses - such as aluminium producers, iron and steel makers, petrol refiners and LNG producers, initially totaling 25% to 33% of permits and rising to 45% by 2020.
7. There will be total offset of the impact on fuel prices on households for 3 years.
8. Agricultural emissions are not included initially but may be included from 2015.
9. There will be a price cap on emissions, that will start at AUD 40 per tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent.
10. Firms will be able to purchase unlimited quantities of emissions allocations (including CERs under the clean development mechanism) from the international market, but will not be able to sell them during the initial years.
11. Reforestation can count as carbon credit, but deforestation and forest degradation do not count as a liability.
Criticism

The national Climate Action Summit of 500 participants representing 140 climate groups Australia wide has condemned the CPRS and agreed to campaign to prevent it becoming law. Major concerns included announced targets, granting of property rights to pollute and providing free permits to major polluters. Summit participants were joined by 2,000 other people in surrounding parliament house to express dissatisfaction with the Rudd Government climate change policies.
Criticism of the targets
1. Greenpeace, the World Wildlife Fund, the Wilderness Society and the Climate Institute were joined by the Greens and other environmentalists in calling for more ambitious 2020 targets of 25 to 45 per cent reductions.
2. Two scientists on the IPCC, one a lead author, said the cuts were inadequate.
3. Professor Barry Brook, the Director of the Research Institute for Climate Change and Sustainability at the University of Adelaide, stated that "the 14% cut in our total emissions by 2020 announced today is such a pitifully inadequate attempt to stop dangerous climate change that we may as well wave the white flag now."
4. Dr Regina Betz, Joint Director of the Centre for Energy and Environmental Markets at UNSW, stated "The proposed 2020 targets of emission reductions of 5 to 15% are, according to the climate science, entirely inadequate for an equitable global response to avoid dangerous global warming."
5. Dr Frank Jotzo, deputy director of the ANU Climate Change Institute, and former advisor to the Garnaut Climate Change Review, said "ruling out a 25% reduction is a mistake, since Australia's overwhelming interest is strong global climate action. An international agreement with deep cuts has just become a little bit more unlikely, as a result of Australia not putting a compatible offer on the table" and "the Treasury modelling has shown that even deep cuts won't carry big economic costs for Australia, if the policies are sound."
Criticism of the costs
1. Australian Chamber of Commerce & Industry chief executive Peter Anderson said his members were "apprehensive" about the scheme because it was "too risky" and warned the costs would be borne not only by emissions-intensive, trade-exposed industries but also by "small and medium businesses through higher energy costs and the flow-on from restructuring of larger industries".
2. Australian Industry Group chief executive Heather Ridout said the scheme was "a big ask and will have a big impact on the Australian economy" and estimated it would add about $7 billion to business costs by 2010.
Other criticism
Other sources of criticism included:
1. Dr Hugh Saddler, Managing Director of Energy Strategies Pty Ltd, stated "the white paper does not include measures to reduce emissions from the major non-energy sectors such as agriculture and land clearing. While it is a good decision not to include these emission sources within the CPRS, it is essential that there be other strong programs specifically directed at these sectors."
2. Mitch Hooke, vocal boss of the Minerals Council of Australia, said his organisation was "profoundly disappointed that the white paper was not better aligned with progress towards a global agreement on reduction commitments, new low emissions technologies and emissions trading schemes in other countries"
3. South Africa's environment minister, Marthinus Van Schalkwyk, has described the scheme as an inadequate "opening bid", and warned that it is not "nearly good enough to bring developing countries to the table".
4. The national climate change adviser, Professor Ross Garnaut, damned the Rudd Government's carbon policy on three main grounds
1. Gross over-compensation of coal fired electricity generators;
2. Taking the possibility of 25% cuts off the table when they are in Australia's best interest;
3. The lack of a principled basis for support of trade-exposed industries;
4. The proposed compensation to industry represents a potential threat to public finances.
Support
Statements of support included:
1. United Nations climate chief says the Government's emissions trading scheme is very encouraging and Australia should be applauded for entering the carbon market.
2. Gerard Henderson, the former Chief-of-Staff to John Howard, has described Rudd's emissions targets as "responsible".
After changes announced in May 2009, some business and environment groups announced that the CPRS was now worth supporting.
Other
Whether or not the Federal Opposition will support the proposed legislation will depend on an independent assessment of the Government's carbon emission scheme it will commission.Without support of some Opposition members in the Senate there is a possibility the enabling legislation may not be passed unless it gains the support of the Greens, Family First and independent senators. If the enabling legislation is not passed, there is a chance that it could be passed if the Government uses it as a trigger for a double dissolution election.
May 2009 changes
On 4 May 2009, the government announced a number of modifications to the proposed Scheme, including a delayed start, a deeper conditional target (25% by 2020, in the event of a global agreement aiming at 450 ppm), more assistance for industry, and a "carbon trust" to enable voluntary action by households.
November 2009 changes
There were a number of significant changes made to the scheme in November 2009 after Malcolm Turnbull negotiated with Prime Minister Kevin Rudd. These changes included huge increases in compensation for polluting industries, including the coal and aluminium smelting industries.
* $4billion is now proposed for the manufacturing sector.
* $1.5billion is now proposed for electricity generators.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
History
In the election year of 2007, both the Liberal-led Coalition government and the Labor opposition promised to introduce carbon trading. Opposition leader Rudd commissioned the Garnaut Climate Change Review on 30 April, while Prime Minister John Howard announced his own plan on 4 June, after the final report of the Prime Ministerial Task Group on Emissions Trading. Labor won the election on 24 November.
Green Paper
The draft Garnaut Report, issued on 4 July, was only one of many inputs into the policy-making process. The Labor government issued a "Green Paper" on 16 July, describing the intended design of the carbon trading scheme. Draft legislation will be released in December 2008, to become law in 2009.
The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme, as outlined in the Green Paper, is a market-based approach to greenhouse gas pollution, to be implemented in 2010 (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 9). The main concern for the Australian government at present is getting the design of such a scheme correct, in order that it will complement the integrated economic policy framework, and need to be consistent with the Government’s commercial strategy (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 10).
The objective of the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme is to meet Australia’s emissions reduction targets in the most flexible and cost-effective way; to support an effective global response to climate change; and to provide for transitional assistance for the most affected households and firms (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 14).
The basis of a Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme is a cap and trade system, and is a way of limiting greenhouse gas pollution, as well as giving individuals and businesses incentives to reduce their emissions (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 11). The first step for the Australian Government is to set a cap on carbon emissions, which must be consistent with longer term goals of reducing Australia’s emissions by 60% compared with 2000 levels by 2050 (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 11).
There are two definite elements of the cap and trade scheme: the cap itself, and the ability to trade (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). The cap is the limit on greenhouse gas emissions imposed by the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme. The system aims at achieving the environmental outcome of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the idea being that capping emissions creates a price for carbon and the ability to trade assures that emissions are reduced at the lowest possible price (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). Setting a limit means that the right to emit greenhouse gases becomes scarce, and scarcity entails a price. The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme will put a price on carbon in a systematic way throughout the economy (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13).
The ‘covered’ sectors are emissions that are subject to the cap, which are specified by the Government under the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). Once this is established, and after setting the cap, the Government then issues permits that are equal to the cap. The Green Paper gives the example “if the cap were to limit emissions to 100 million tonnes of Co2-e in a particular year, 100 million ‘permits’ would be issued that year” (2008, 12). With each tonne of emissions from a firm that is responsible for emissions covered by the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme, they are required to acquire and surrender a permit (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). As yet there are no limits or caps imposed on individual emitters or sectors.
There are around 1,000 firms that are under obligations from the Scheme, which covers the bulk of national emissions. This means that 99% of all firms in Australia will not need to purchase permits for their emissions.
However, the price of emissions resulting from the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme will increase the cost of those goods and services that are most emissions intensive (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13). This means that there will be a change across the prices of goods and services across the economy, reflecting how emission-intensive the goods or service is. This therefore provides businesses and consumers with incentives to use and invest in low-emissions technologies.
The second essential element of a cap and trade scheme is the ability to trade. Since carbon pollution permits will be tradeable, the price of permits will be determined by the market (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13). The main idea behind this part of the scheme is that a firm who can undertake abatement more cheaply than the permit price will do so, and that a company will pay for permits if the cost to it of lowering its emissions exceeds the cost of the permits. By trading among themselves, firms achieve the scheme cap at the least cost to the economy (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 13).
The cap will only achieve the desired environmental objectives if it is enforced. This means that firms responsible for emissions covered by the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme must monitor their emissions and report them accurately to government (Department of Climate Change, 2008, 12). Arrangements for the assurance of reported emissions data are required.
Treasury report on the economics of climate change mitigation
The Australian Treasury's report on the economics of climate change mitigation was released on October 30, 2008. The report is considered a key input for determining the structure and targets for the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme.
The Treasury’s modeling demonstrated that early global action to reduce carbon emissions would be less expensive than later action and stated that a market-based approach allows robust economic growth into the future as emissions fall.
The report also stated that:
* many of Australia’s industries would maintain or improve their competitiveness under an international agreement to combat climate change
* even ambitious goals would have limited impact on national and global economic growth
* Australia and the world can continue to prosper while making the emission cuts required to reduce the risks of dangerous climate change.
* Households would face increased prices for emission-intensive products such as electricity and gas, however real household income would continue to grow.
* Strong coordinated global action would reduce the economic cost of achieving environmental objectives, reduce distortions in trade-exposed sectors, and provide insurance against climate change uncertainty.
* There are advantages to Australia acting early if emission pricing expands gradually across the world: economies that defer action face higher long-term costs, as global investment is redirected to early movers.
* Australia’s aggregate economic costs of mitigation are small, although the costs to sectors and regions vary. Growth in emission-intensive sectors slows and growth in low- and negative-emission sectors accelerates.
* Allocation of some free permits to emission-intensive trade-exposed sectors, as the Government proposes, eases their transition to a low-emission economy in the initial years.
* Broadly-based market-oriented policies, such as emissions trading, allow the market to respond as new information becomes available.
White Paper
The White Paper was released on 15 December 2008. The White Paper included the Rudd Labor government's targets for Greenhouse gas emission reductions, 5% below 2000 by 2020 on a unilateral basis or up to 15% below 2000 by 2020 if also agreed by the other major emitters. This compares to the 25 to 40% cut compared to 1990 emissions recommended by the IPCC as needing to be made by developed countries to keep CO2 below 450 ppm and to have a reasonable chance of keeping global warming at less than a 2 degree Celsius increase above pre-industrial times.
The White Paper also set an indicative national emissions trajectory for the first few years of the scheme:
* in 2010-11, 109% of 2000 levels;
* in 2011-12, 108% of 2000 levels;
* in 2012-13, 107% of 2000 levels.
For comparison, in 2006, Australia's emissions were 104% of 2000 levels (under Kyoto accounting).
Some of the features of the emissions trading scheme proposed include:
1. an output as opposed to consumption based scheme
2. A modelled carbon price range of AUD 20 to AUD 40 per tonne of carbon.
3. Less than 1,000 businesses will have to account for their emissions and buy or be allocated free permits.
4. AUD 4.8 billion of assistance (in the form of free permits) for the most polluting electricity generators.
5. Financial assistance to compensate low and middle income families from increased costs.
6. Free permits to emissions-intensive, trade-exposed businesses - such as aluminium producers, iron and steel makers, petrol refiners and LNG producers, initially totaling 25% to 33% of permits and rising to 45% by 2020.
7. There will be total offset of the impact on fuel prices on households for 3 years.
8. Agricultural emissions are not included initially but may be included from 2015.
9. There will be a price cap on emissions, that will start at AUD 40 per tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent.
10. Firms will be able to purchase unlimited quantities of emissions allocations (including CERs under the clean development mechanism) from the international market, but will not be able to sell them during the initial years.
11. Reforestation can count as carbon credit, but deforestation and forest degradation do not count as a liability.
Criticism

The national Climate Action Summit of 500 participants representing 140 climate groups Australia wide has condemned the CPRS and agreed to campaign to prevent it becoming law. Major concerns included announced targets, granting of property rights to pollute and providing free permits to major polluters. Summit participants were joined by 2,000 other people in surrounding parliament house to express dissatisfaction with the Rudd Government climate change policies.
Criticism of the targets
1. Greenpeace, the World Wildlife Fund, the Wilderness Society and the Climate Institute were joined by the Greens and other environmentalists in calling for more ambitious 2020 targets of 25 to 45 per cent reductions.
2. Two scientists on the IPCC, one a lead author, said the cuts were inadequate.
3. Professor Barry Brook, the Director of the Research Institute for Climate Change and Sustainability at the University of Adelaide, stated that "the 14% cut in our total emissions by 2020 announced today is such a pitifully inadequate attempt to stop dangerous climate change that we may as well wave the white flag now."
4. Dr Regina Betz, Joint Director of the Centre for Energy and Environmental Markets at UNSW, stated "The proposed 2020 targets of emission reductions of 5 to 15% are, according to the climate science, entirely inadequate for an equitable global response to avoid dangerous global warming."
5. Dr Frank Jotzo, deputy director of the ANU Climate Change Institute, and former advisor to the Garnaut Climate Change Review, said "ruling out a 25% reduction is a mistake, since Australia's overwhelming interest is strong global climate action. An international agreement with deep cuts has just become a little bit more unlikely, as a result of Australia not putting a compatible offer on the table" and "the Treasury modelling has shown that even deep cuts won't carry big economic costs for Australia, if the policies are sound."
Criticism of the costs
1. Australian Chamber of Commerce & Industry chief executive Peter Anderson said his members were "apprehensive" about the scheme because it was "too risky" and warned the costs would be borne not only by emissions-intensive, trade-exposed industries but also by "small and medium businesses through higher energy costs and the flow-on from restructuring of larger industries".
2. Australian Industry Group chief executive Heather Ridout said the scheme was "a big ask and will have a big impact on the Australian economy" and estimated it would add about $7 billion to business costs by 2010.
Other criticism
Other sources of criticism included:
1. Dr Hugh Saddler, Managing Director of Energy Strategies Pty Ltd, stated "the white paper does not include measures to reduce emissions from the major non-energy sectors such as agriculture and land clearing. While it is a good decision not to include these emission sources within the CPRS, it is essential that there be other strong programs specifically directed at these sectors."
2. Mitch Hooke, vocal boss of the Minerals Council of Australia, said his organisation was "profoundly disappointed that the white paper was not better aligned with progress towards a global agreement on reduction commitments, new low emissions technologies and emissions trading schemes in other countries"
3. South Africa's environment minister, Marthinus Van Schalkwyk, has described the scheme as an inadequate "opening bid", and warned that it is not "nearly good enough to bring developing countries to the table".
4. The national climate change adviser, Professor Ross Garnaut, damned the Rudd Government's carbon policy on three main grounds
1. Gross over-compensation of coal fired electricity generators;
2. Taking the possibility of 25% cuts off the table when they are in Australia's best interest;
3. The lack of a principled basis for support of trade-exposed industries;
4. The proposed compensation to industry represents a potential threat to public finances.
Support
Statements of support included:
1. United Nations climate chief says the Government's emissions trading scheme is very encouraging and Australia should be applauded for entering the carbon market.
2. Gerard Henderson, the former Chief-of-Staff to John Howard, has described Rudd's emissions targets as "responsible".
After changes announced in May 2009, some business and environment groups announced that the CPRS was now worth supporting.
Other
Whether or not the Federal Opposition will support the proposed legislation will depend on an independent assessment of the Government's carbon emission scheme it will commission.Without support of some Opposition members in the Senate there is a possibility the enabling legislation may not be passed unless it gains the support of the Greens, Family First and independent senators. If the enabling legislation is not passed, there is a chance that it could be passed if the Government uses it as a trigger for a double dissolution election.
May 2009 changes
On 4 May 2009, the government announced a number of modifications to the proposed Scheme, including a delayed start, a deeper conditional target (25% by 2020, in the event of a global agreement aiming at 450 ppm), more assistance for industry, and a "carbon trust" to enable voluntary action by households.
November 2009 changes
There were a number of significant changes made to the scheme in November 2009 after Malcolm Turnbull negotiated with Prime Minister Kevin Rudd. These changes included huge increases in compensation for polluting industries, including the coal and aluminium smelting industries.
* $4billion is now proposed for the manufacturing sector.
* $1.5billion is now proposed for electricity generators.
From http://en.wikipedia.org/
Langganan:
Postingan (Atom)